- All Drug Categories
- Home
- Anti-cancer Drugs
- Healthcare Products
- Medical Information
- Statement
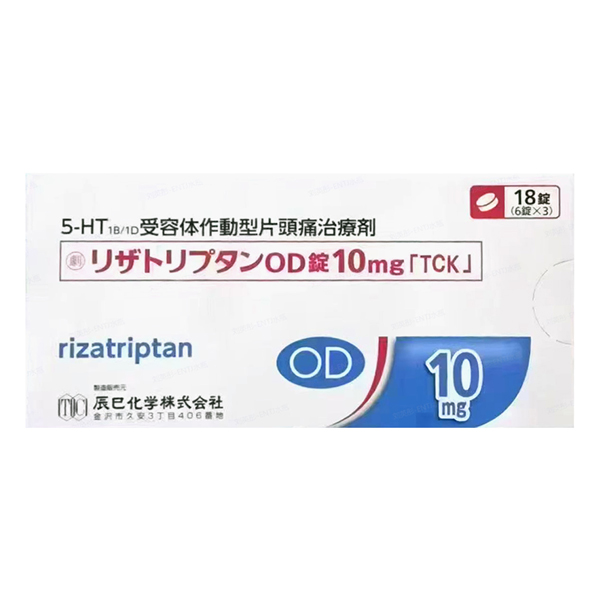
All Names: Rizatriptan Benzoate Orally Disintegrating Tablets、Rizatriptan OD Tablets「TCK」、利扎曲普坦、リザトリプタンOD錠
Indications:Adult patients diagnosed with migraine by neurologists or related specialists according to the International Headache Society (IHS) diagnostic criteria. Not suitable for preventive treatment of migraine, and also prohibited for patients with familial hemiplegic migraine, sporadic hemiplegic migraine, basal migraine, or ophthalmoplegic migraine.
Manufacturer:Japan Chensi
Customs Clearance Procedure:If the customs requires the package for customs clearance, please pay the customs clearance fee according to the content of EMS SMS and customs regulations.
Lizariptan is a highly selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist, belonging to the triptan class of prescription drugs, specifically used for acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura.
1、 Drug name
1. Common name: Liraglutide Benzoate Oral Disintegrating Tablets
2. Product Name: Lozatriptan OD Tablets 10mg
2、 Indications
Used to treat acute attacks of migraine with or without premonitory symptoms.
3、 Specifications and characteristics
1. Specification: Each tablet contains 14.53mg of linatriptan benzoate (equivalent to 10mg of linatriptan).
2. Appearance: White plain tablet, diameter 9.0mm, thickness 2.6mm, weight approximately 200mg. The tablet is printed with the identification code "TU277".
4、 Main components
Active ingredient: Liraglutide benzoate.
5、 Usage and dosage
1. Adult standard dose: 10mg each time, taken orally during migraine attacks.
2. Additional dose: If the effect is not sufficient, an additional dose can be administered at least 2 hours after the first dose.
3. Daily dose limit: The total daily dose should not exceed 20mg.
4. Usage: This product is an orally disintegrating tablet that can be placed on the tongue and swallowed after disintegration, without the need for water; It can also be served by water delivery.
6、 Dose adjustment
1. The specifications of this product are fixed and there is no routine dose adjustment based on efficacy.
2. Patients with renal or liver dysfunction need to follow the requirements of the "Special Population Medication" section.
7、 Medication precautions
1. Medication timing: Only used during migraine attacks and should not be used for prevention.
2. Invalid treatment: If a single dose is completely ineffective, additional medication should not be taken for the same episode, and the cause of the headache should be re evaluated.
3. Before and after meals: Food can delay the absorption rate of drugs (prolong Tmax), but it does not affect the total absorption amount (AUC and Cmax). Therefore, it can be taken before and after meals, but for faster effectiveness, it is recommended to take it on an empty stomach.
4. Omission: This medication is used as needed during an attack, without a fixed medication schedule, and there is no concept of "omission".
5. Vomiting after taking medication: If vomiting occurs shortly after taking medication, the medication may not be fully absorbed and the therapeutic effect may be insufficient. But the daily dose limit (20mg) should be followed, and it is not recommended to take it immediately without consulting a doctor.
6. Operation warning: drowsiness may occur after taking medication, and driving or operating dangerous machinery should be avoided.
7. Overdose: The main symptoms of overdose are drowsiness, dizziness, hypertension, etc. Once it occurs, immediate medical attention should be sought, which may require gastric lavage, activated carbon adsorption, and electrocardiogram monitoring.
8、 Medication for special populations
1. Pregnant women: Use only when the benefits of treatment outweigh the potential risks.
2. Breastfeeding women should consider the necessity of treatment and the benefits of breastfeeding, and weigh whether to continue breastfeeding or discontinue medication. Animal experiments have shown that drugs can be excreted through breast milk.
3. Children: There is currently no relevant clinical research data available.
4. Elderly individuals (≥ 65 years old): There is no significant difference in pharmacokinetics compared to young adults, and dose adjustment is not necessary.
5. Patients with liver dysfunction: It is contraindicated for patients with severe liver dysfunction. Patients with moderate to mild liver dysfunction may have elevated blood drug concentrations and should be cautious.
6. Patients with renal insufficiency: Do not use hemodialysis. Non dialysis patients with renal insufficiency do not require dose adjustment.
7. High risk cardiovascular patients: Patients with a history of ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, uncontrolled hypertension, etc. should avoid or use with caution (see contraindications for details).
9、 Adverse reactions
1. Common adverse reactions (≥ 1%): drowsiness (approximately 7.7%).
2. Other adverse reactions include weakness/fatigue, palpitations, nausea, dizziness, decreased sensation, dry mouth, neck pain/stiffness, elevated CK, photophobia, etc.
3. Serious side effects (requiring immediate medical attention):
(1) Allergic shock and angioedema.
(2) Symptoms of ischemic heart disease (such as chest pain, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction).
(3) Cerebrovascular disorders (such as cerebral infarction, transient ischemic attack).
(4) Epilepsy like seizures.
(5) Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens Johnson syndrome (SJS).
(6) Drug overdose headache (caused by long-term and frequent use).
10、 Contraindications
1. Individuals who are allergic to any ingredient of this product.
2. Individuals with a history of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease (including angina pectoris, coronary artery spasm), or related symptoms/signs.
3. Individuals with a history of cerebrovascular disorders or transient ischemic attacks.
4. Patients with peripheral vascular disease.
5. Uncontrolled hypertensive patients.
6. Patients with severe liver dysfunction.
7. Hemodialysis patients.
8. Patients who are currently using or have used monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) within 2 weeks of discontinuation.
9. Patients currently using propranolol (propranolol).
10. Patients who are currently using other 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists (such as sumatriptan, zolpidem, etc.) or ergotamine/ergotamine derivative preparations.
11. Patients with familial hemiplegic migraine, basal migraine, or ophthalmoplegic migraine.
11、 Drug interactions
1. Prohibition of joint use:
(1) Other 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists (such as triptans) should be administered at least 24 hours apart.
(2) Ergotamine/ergotamine derivatives: The interval should be at least 24 hours.
(3) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
(4) Propranolol.
2. Cautious combination:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): may increase the risk of developing serotonin syndrome.
12、 Storage method
1. Store at room temperature. Avoid contact with children.
2. Remove the tablets from the aluminum-plastic blister pack before taking them to prevent accidental ingestion of the packaging and esophageal injury.
13、 Manufacturer
1. Marketing authorization holder/manufacturer/seller: Chensi Chemical Co., Ltd.
2. Address: 406 Ku'an 3-chome, Kanazawa City, Japan.
Rizatriptaninformation